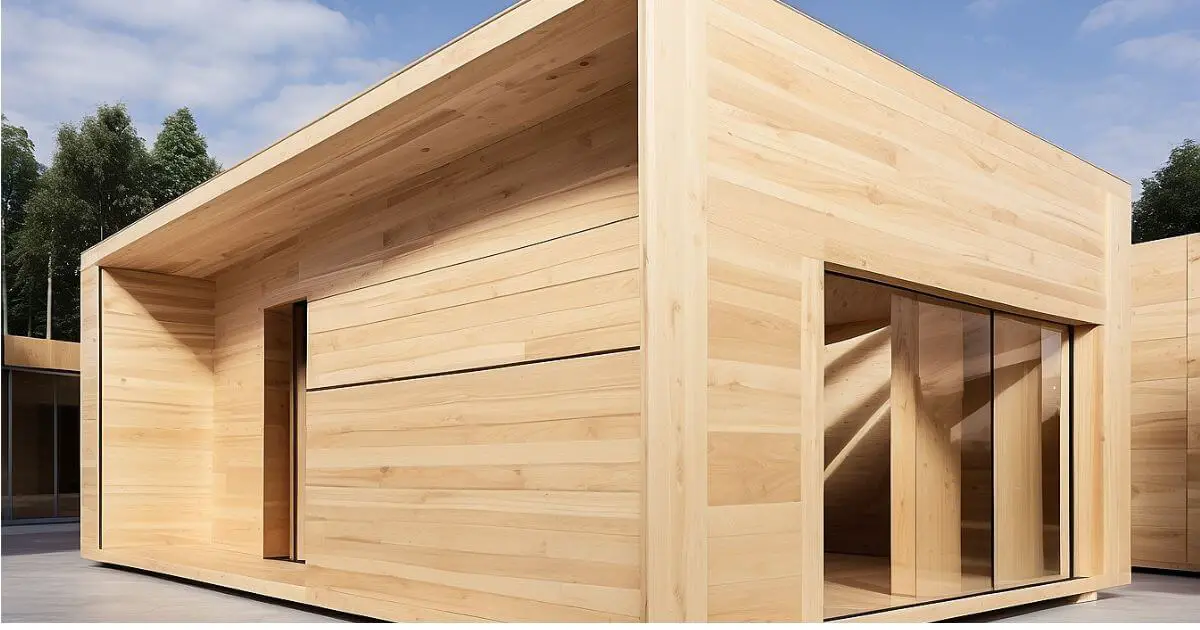
What is Cross-Laminated Timber?
Cross-laminated timber (CLT), also known as X-Lam, is an engineered timber product. CLT is made by gluing together multiple layers (usually three, five, or seven layers) of solid lumber using hydraulic or vacuum pressure. Each wooden board is perpendicular to each other, giving strength and stability to the structure.
CLT is an amazing wood product that was introduced in the early 1990s in Austria and Germany. It is becoming popular day by day, and now it is used all over the world.
Cross-Laminated Timber Uses
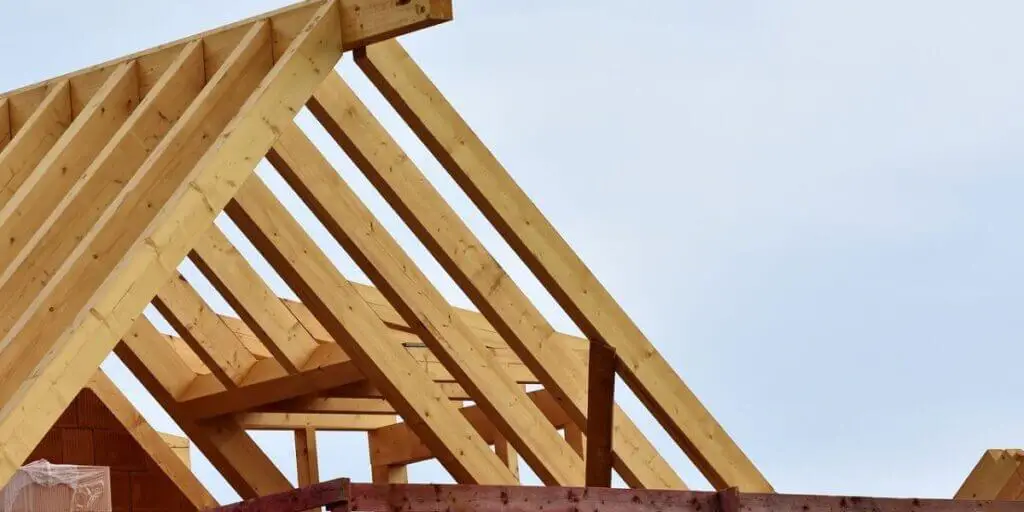

Flooring and Decking
Cross-laminated wood is a durable and excellent choice for wood floors. It has been in use for many decades. CLT flooring costs may be less than traditional steel or concrete. Some flooring experts say that the thickness of CLT should be at least 4 inches to make a better floor.
CLT Beams
Beams and pillars play an important role in building a house. Beams should be strong as they bear the entire weight of the roof. Apart from this, one also has to face strong winds and storms.
In this respect, CLT is significantly superior to traditional wood and other wood materials because the hollow and knotty parts of the wood are removed during the CLT manufacturing process.
Roofing
Cross-laminated timber is known for insulation, optimum air humidity, soundproofing, excellent fire protection, high load-bearing capacity and earthquake-resistant construction, making it superior for use on rooftops. It is also used with glulam wood as a hybrid construction.
Walls
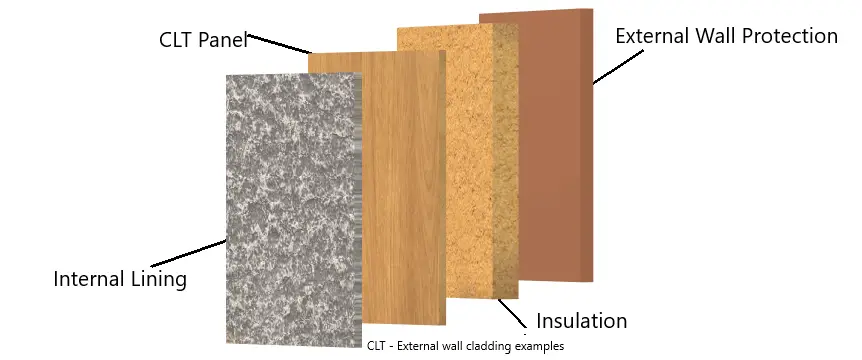
CLT is used to create a strong wall, although it is installed with several other layers, such as weather protection (on the outermost wall), insulation, CLT panels, and internal lining (on the inside).
CLT is an environmentally friendly construction material, and there is no harm in its use. This material is employed to reduce energy consumption.
The uses of cross-laminated wood depend on the number of layers present in it. It can be divided into 3 categories
| # | Thickness | No. of Lumber | Uses |
| Minimum | 40 to 51MM | 3 Layers | Walls, Secondary construction |
| Standard | 140 to 160MM | 5 Layers | Floor, Beams, and Roofing |
| Maximum | 400 to 500MM | 11 Layers | Bridge and Decks |
CLT Appearance
CLT can be yellowish or whitish with brown as it is made primarily from solid wood of pine, spruce and larch. There is no change in color and properties during CLT manufacturing.

Cross-Laminated Timber Advantages
High Load Capacity
Cross-laminated timber is a high-load capacity construction material. So, it is an excellent choice for beams, bridges, and walls. It is stronger and more durable than other wood construction materials.
Easy to Install
CLT panels are easy to work with hand and machine tools. CLT panels are often used in precast or modular construction, which can significantly speed up the building process.
Excellent Thermal Properties
CLT panels provide excellent thermal insulation. The impressive performance of CLT is attributed to its multiple layers of wood. CLT has a thermal conductivity of 0.13W/mK, surpassing that of traditional wood logs, steel, and concrete.
This is particularly beneficial for regions experiencing very cold and hot weather, as CLT helps maintain room temperature.
Fire Protection
CLT panels have good fire-resistant properties. The outer layer of CLT behaves as a self-insulating material and creates a charring barrier, which prevents the oxygen( helps to increase the fire) from the outside.
Environmental Advantages
CLT is made from wood, a renewable resource. The manufacturing process also requires less energy than traditional construction materials such as concrete and steel.
Compared to concrete and other construction materials, an average reduction of 26.5% in global warming potential has been achieved in CLT buildings.
Less Waste
CLT panels are available in a wide range of shapes and sizes. The manufacturing company makes it based on different purposes and applications. As a result, the production of CLT generates minimal waste material.
Cross-laminated Timber Disadvantages
Cost
Cross-laminated wood is more expensive than traditional construction, such as steel or concrete. However, the overall cost-effectiveness depends on various factors, including project size, location, and availability of materials.
Limited Market Availability
Although the popularity of CLT is growing, it may not be as readily available in all regions compared to traditional construction materials. Limited market availability can impact the feasibility of using CLT in certain projects.
Moisture Sensitivity
CLT is sensitive to moisture, and prolonged exposure to moisture can cause swelling or warping. Proper moisture management and protection are important to maintain the structural integrity of CLT.
Transportation Challenges
CLT panels can be large and heavy, requiring special transportation considerations. Transportation costs and logistics challenges may arise.
Conclusion
Cross-laminated timber is an excellent engineering construction material. CLT is a great material for the new construction era. It has some flaws and strengths, which I have tried to cover. Even with some flaws, it is a better material; you should use it.
Read another post

