What is a blockboard?
The core of the blockboard Plywood consists of blocks or strips of wood, and all these wooden strips are glued between two thin veneer panels under high heat and pressure.
Blockboard is also known as Lumber Core Plywood. It is a durable, inexpensive material that is designed for indoor use or where the application does not face moisture.
Blockboard is known for its excellent bending strength and screw-hold ability. The way this plywood is made gives it strength.
Uses of Blockboard
Blockboard is a versatile material used for tables and benches, beds, wardrobes, doors, partitions, lengthy wall panels, shelves, and more. It is an easy-to-find strong board, so it is most commonly used for making doors.
It is a lightweight product that is used in making almost all types of furniture. Although it was designed for indoor purposes. But it is also present in WBP grade which can be used in humid places and open weather also.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lumber Core Plywood
Advantages
1. Excellent strength and durability
Blockboard has excellent strength and durability than Medium-density fibreboard (MDF) and particle board of the same thickness.
2. Inexpensive
Blockboard is an inexpensive material, widely used for furniture. Its cost is much less than solid wood and plywood.
3. Wide range and availability
Blockboard is available in many different thicknesses, sizes, and grades. You can choose them as per your requirement.
4. Workability
Blockboards are easy to work with both hand and machine tools. Glues and finishes well. Like solid wood, blockboards can also take paint and a laminate coat on the surface.
Disadvantages
1. Not for outdoor use
Blockboard is not suitable for outdoor purposes as it tends to deteriorate very quickly when it comes in contact with moisture and water.
The glue used to make it is not waterproof. Therefore, prolonged exposure to moisture causes the blockboard to swell.
For applications that are exposed to moisture and weather, moisture-resistant grade Blockboard can be a good choice, which is a bit expensive.
2. Voids and Gaps
There are voids or gaps after each wood strip in the core of the blockboard. Through these gaps, moisture and insects easily enter the core and start spoiling the plywood.
These voids or gaps have to be covered from the outside with a thin strip of wood with glue.
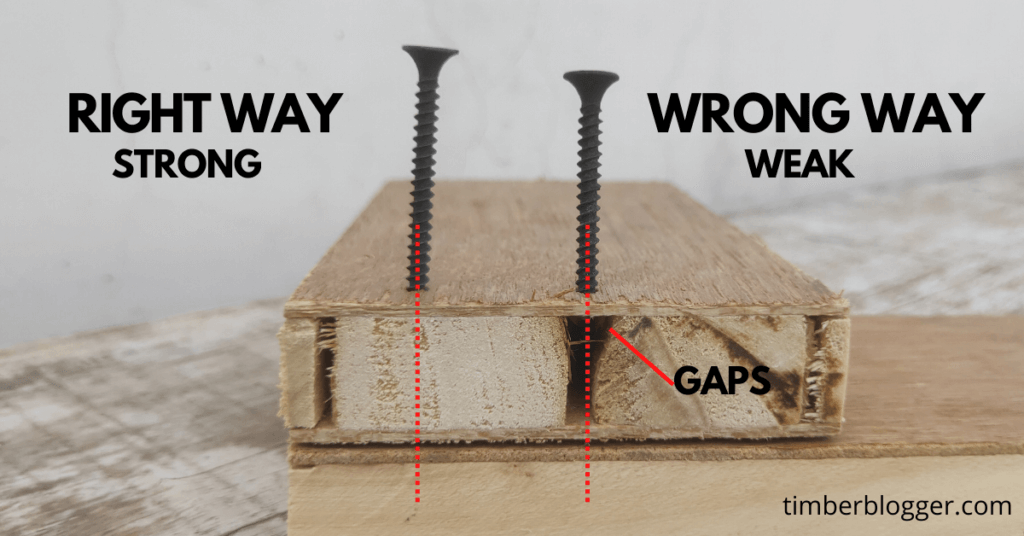
3. Nails and screw holding properties
The blockboard holds the nail and screw well when this nail is being driven into the wood strip of the core. But it does not always happen that, when the nail or screw goes into the voids or gaps, then it does not hold well, so the application becomes weak.
4. Low-quality core
Defected wood strips may be filled in the core of low-quality blockboard which gets spoiled very fast. Due to the defective strips being inside, they cannot be seen.
Poor quality blockboard cores are filled with defected and rotted wood strips that wear out very quickly. It is very difficult to recognize them because the defects are in the core.
Types of Blockboards
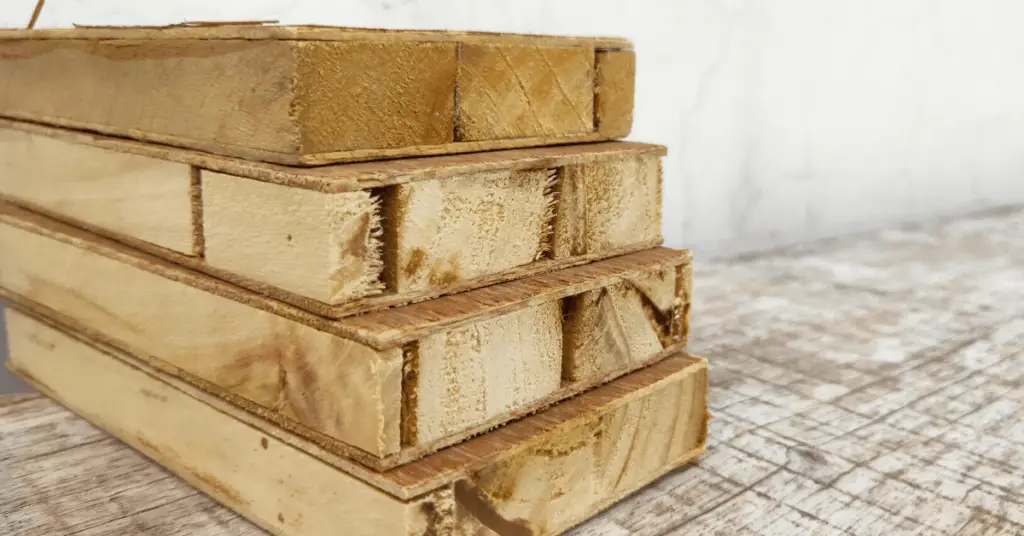

There are many types of blockboards. They are divided based on their quality, use, types of wood, and types of glue used for the core. We can classify blockboards by grade and by the types of wood used.
There are mainly two types of blockboard based on Grade and uses
1. Interior Grade Blockboard
The Interior Grade Blockboard is designed for indoor use. It can be used for partitions, ceilings, tables, benches, shelving, paneling, etc. To make it durable, it has to be covered with paint or laminate.
Interior Grade Blockboard is also known as MR-grade Blockboard. Because it is assembled with MR glue, which can withstand moisture for a time.
2. Exterior Grade Blockboard
Exterior Grade Blockboard is designed for outdoor use. This board can be used for decks, sheds, outdoor furniture, benches, and racks.
Exterior Grade Blackboard is made from Boiling Waterproof (BWP) glue, which has the highest resistance to water and weather for a long time. Its stability can be compared to marine-grade plywood.
Blockboard can also be divided based on the wood used.
There are two types of wood used to make blockboard: softwood, and hardwood. Both types of blockboard have different physical properties and use.
1. Softwood Blockboard
Softwood blockboards are made from softwoods such as Cedar, Douglas fir, or redwood. Mainly they are used for general work.
The price and weight of a softwood blockboard are less than a hardwood blockboard.
2. Hardwood Blockboard
Hardwood Blockboards are made from hardwood such as Birch, Oak, Mahogany, Maple, etc. Wood strips may be up to about 40mm wide.
Hardwood Blockboard can be stronger than steel in static bending strength.
How is blockboard made?
Wood is used as the raw material to make the blackboard. There can be several species of wood. These are some of the basic steps that are followed to make a blackboard.
1. Harvest and Seasoning
In the first phase, the mature trees are harvested from the forest and the tree logs are stored for one or two seasons so that the extra moisture gets dried up. Recommends moisture content of 5% – 15% by weight for plywood.
It is important to have the correct amount of moisture content in the wood before proceeding to the next steps.
2. Debarking and Slicing Wood
In the debarking process, the bark is removed from the log. In today’s era, debarking is done in the forest during the cutting of trees by modern machines.
After debarking, the logs are cut into thin strips that are used to form the core of the blockboard. Generally, the thickness of the wood strip is 13 to 30 mm. The thickness of the strip also depends on the type of plywood.
3. Peeling the Logs
In this step, veneers (thin layers of wood) are made for the front and back faces of the blockboard, which hold the wood strip of the core.
Logs are peeled using a rotary lathe. Generally, the standard thickness of the veneer is 0.15mm to 0.2mm.
4. Sizing and Grading
Once the wood is peeled off, they need to be cut to size and go through an initial grading process. The wooden strips and veneers are divided into grades based on quality to make different grades of blockboards. Defect-free wood strips and veneers are selected to make A-grade blockboards.
5. Application of Glue and Lay-Up
In this process, the veneer sheet is passed through the gluing machine, and the wood strip is laid on top of it. After this, the whole structure is again passed through the gluing machine, and then the veneer sheet of the second side is applied.
6. Cold and Hot Pressing
After gluing all the raw materials together, the panel looks like a blockboard, but it is not ready yet.
In this process, the incomplete structure is passed through the cold and hot pressing machine. So that all the layers are glued together well. After this step, it is left for 24 to 48 hours to dry well in the drying chamber.
7. Trimming, Sanding, and Finishing
In this process, the excess veneer is trimmed so that the board has square edges. The boards are sanded using a large, industrial sander to clean the surface and make it smooth.
8. Packaging
In this final step, the blockboard is packed and sent to the dealer.
Common Questions
Are Blockboard and plywood the same?
No, blockboard and plywood are different materials. The core of the blockboard is made of wood strips, while the core of the plywood is made of multiple thin veneers.
Plywood is more durable, stable, and stronger than blockboard. Plywood is also more expensive than blockboard. The method and purpose of making these two materials are different.
The other differences between blockboard and plywood are as follows in the table below.
| # | Blockboard | Plywood |
| Durability | Durable for interior uses | Extreme durable for interior and exterior |
| Available in thicknesses | 12mm, 15mm, 19mm, 25mm, 30mm, 35mm, 40mm, 45mm, and 50mm | 1/2-inch to 3/4 inches |
| Price | Inexpensive | It can be expensive |
| Bending properties | It does not bend like plywood. | It is flexible and bends easily. |
| Uses | Sheathing for roofs, floors, and walls. | Flooring, Interior Walls, Exterior Wall Sheathing, Furniture, Guitars, and So Much More |
Is Blockboard Durable?
The answer may not be straightforward. Because the durability of the board depends on the type of the board and the raw material that is used to make it.
Some high-quality blockboards are very durable, whereas low-quality boards get spoiled after a few years.
The core of the high-quality blockboard is made of A-grade and B-grade wood strips and all wood strips are glued well, which is durable and stable. Whereas defective wood strips are filled in low-quality blackboard.
Is Blockboard waterproof?
Blockboard is not completely waterproof. But BWP-grade blockboard (made with Boiling waterproof glue) has the highest resistance to water and is considered to be completely waterproof.
But a regular blockboard (which is known as MR-grade and is used for indoor applications) does not have good moisture resistance. It can withstand a little moisture for a short time.
For a blockboard to be durable for a long time, you need to do proper sealing of the board.

